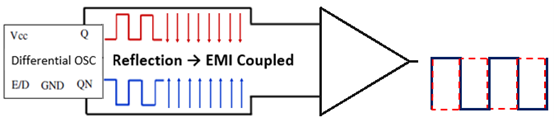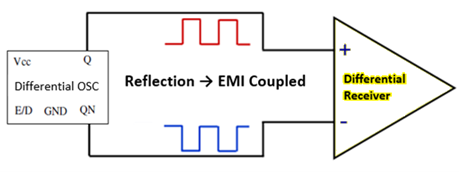
LVPECL: Low-Voltage Positive Emitter-Coupled Logic
LVPECL is an optimized version of PECL that uses a 3.3V positive supply instead of 5V. PECL and LVPECL are differential signaling systems mainly used in high-speed and clock distribution circuits. A common misconception is that PECL devices are slightly different from ECL devices. In fact, every ECL device is also a PECL device.
LVDS: Low-Voltage Differential Signaling
LVDS is an electronic signal system that can meet today’s high-performance data transmission needs. When the system power supply voltage is reduced to 2V, LVDS is suitable for TFT LCD display devices with higher resolution than SVGA. It has been widely incorporated into a variety of devices and can be embedded in FPGA, ASIC or other components.
HCSL: High-Speed Current Steering Logic
HCSL is an interface standard for cable-based, short-distance serial high-speed data transmission. One of its most exclusive applications is the PCI Express (PCIe) physical driver. This is where the HCSL driver stage is integrated into the chipset to connect individual PCIe components, like a graphics card to host processor.
The advantages are: